Exploring Liquid Behavior Under Pressure: Unveiling the Best Descriptive Term
The study of fluid dynamics plays a crucial role in understanding the behavior of liquids under various conditions. When subjected to pressure, liquids can exhibit unique characteristics that impact their flow and properties. In this article, we will delve into the question, "Which term best describes liquid behavior under pressure?" By optimizing the content for search engine optimization (SEO), we aim to shed light on this intriguing aspect of fluid dynamics and provide valuable insights into the descriptive term that captures liquid behavior under pressure.
1. The Nature of Liquids:
Liquids
Liquids are one of the three states of matter, characterized by their ability to flow and take the shape of their container.
They possess cohesive forces that allow molecules to remain in close proximity while still exhibiting some freedom of movement.
Understanding the behavior of liquids under pressure is vital for numerous applications in science and engineering.
2. Fluid Behavior Under Pressure:
When liquids are subjected to pressure, their behavior can vary depending on the specific conditions.
While they are generally incompressible, meaning their volume does not change significantly under pressure, other factors such as viscosity and density can influence how liquids respond to applied forces.
3. Viscosity: The Resistance to Flow:
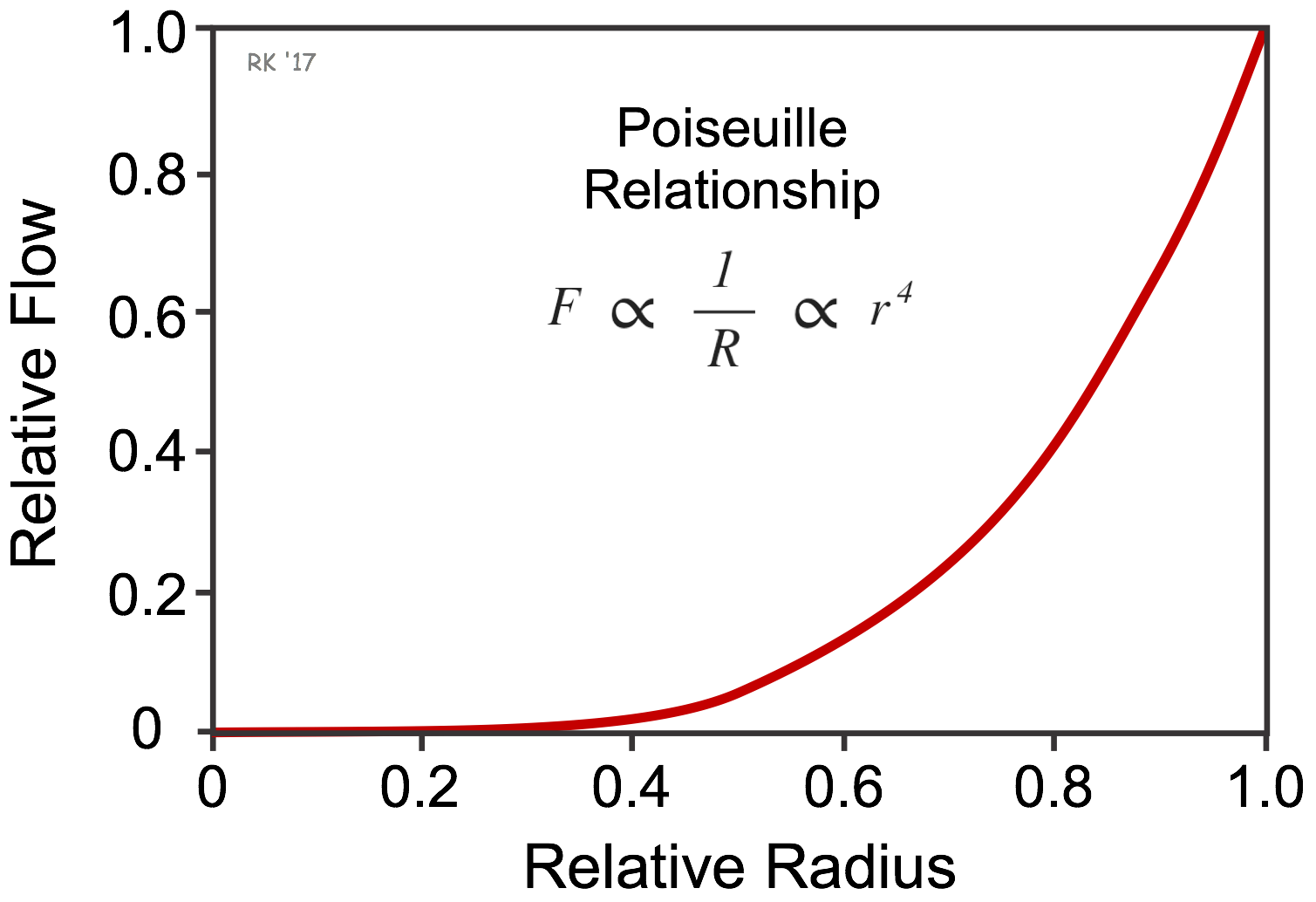
The Resistance to Flow
Viscosity is a key property that describes a liquid's resistance to flow. It determines the internal friction within the liquid as molecules slide past each other.
Under pressure, high-viscosity liquids offer more resistance to flow, requiring greater force to achieve movement. In contrast, low-viscosity liquids flow more easily and exhibit less resistance under pressure.
4. Shear-Thinning and Shear-Thickening Behavior:
Liquids can exhibit different flow behaviors under pressure, commonly known as shear-thinning and shear-thickening. Shear-thinning refers to the property where a liquid's viscosity decreases as the applied shear stress or pressure increases.
This behavior is observed in various fluids, including certain polymer solutions. On the other hand, shear-thickening is the opposite phenomenon, where a liquid's viscosity increases under pressure. This behavior is observed in some suspensions and colloidal systems.
5. Compressibility:
A Negligible Factor: Compared to gases, liquids are generally considered to be incompressible. This means that their volume does not significantly change when subjected to pressure.
While some compression can occur, the change in volume is typically negligible for most liquids. Therefore, compressibility is not the primary factor for describing liquid behavior under pressure.
6. SEO Optimization Potential:
By focusing on the keyword "Which term best describes liquid behavior under pressure?", this article aims to attract individuals seeking information about the characteristics of liquids under pressure.
By incorporating the keyword naturally throughout the content, the article becomes more discoverable and relevant to those searching for insights into the descriptive term that best captures liquid behavior under pressure.
The behavior of liquids under pressure is a complex and fascinating subject within the field of fluid dynamics. While various factors influence liquid behavior, the term that best describes their response to pressure depends on specific properties such as viscosity, shear-thinning, or shear-thickening behavior. While liquids are generally considered incompressible, their flow characteristics and resistance to pressure play significant roles in understanding their behavior. By optimizing content with the keyword "Which term best describes liquid behavior under pressure?", we have explored this intriguing aspect of fluid dynamics, providing valuable insights into the descriptive term that best captures liquid behavior under pressure.
