Which Scenario Adheres to the Law of Conservation of Energy? Exploring Energy Conservation Principles
The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental principle in physics that states that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed from one form to another. In this article, we delve into various scenarios to understand which ones adhere to this important law. By exploring different examples, we aim to provide a clear understanding of how the Law of Conservation of Energy applies in real-life situations.

Law of Conservation of energy - example tree
I. Understanding the Law of Conservation of Energy
1. Introduction to the Law of Conservation of Energy: Define the Law of Conservation of Energy and its significance in the field of physics. Explain the concept of energy conservation and its implications in various systems.
2. Forms of Energy: Discuss different forms of energy, such as kinetic energy, potential energy, thermal energy, and more, to provide a comprehensive understanding of the types of energy involved in conservation.
II. Scenarios Illustrating the Law of Conservation of Energy
1. Pendulum Swing: Explain how a pendulum swing adheres to the Law of Conservation of Energy, demonstrating the transformation between potential and kinetic energy throughout its motion.
2. Roller Coaster Ride: Describe how a roller coaster ride adheres to the Law of Conservation of Energy, with the conversion between potential and kinetic energy as the coaster moves along its track.
3. Bouncing Ball: Illustrate how the Law of Conservation of Energy applies to a bouncing ball, with the conversion between potential and kinetic energy during each bounce.
4. Waterfall: Examine how the Law of Conservation of Energy operates in a waterfall, with the transformation of potential energy to kinetic energy as water falls from a higher to a lower elevation.
III. Scenarios Not Adhering to the Law of Conservation of Energy
1. Perpetual Motion Machine: Highlight the concept of perpetual motion machines and explain why they do not adhere to the Law of Conservation of Energy due to the creation or destruction of energy.
2. Energy Losses in Mechanical Systems: Discuss situations where energy losses occur due to factors such as friction, air resistance, and other non-conservative forces, resulting in a violation of energy conservation.
IV. Applications and Implications of Energy Conservation
1. Energy Conservation in Everyday Life: Discuss the importance of energy conservation in our daily lives, including energy-efficient technologies, renewable energy sources, and the reduction of energy waste.
2. Environmental Impact: Explore how adhering to the Law of Conservation of Energy can contribute to environmental sustainability by reducing energy consumption and minimizing the impact on natural resources.
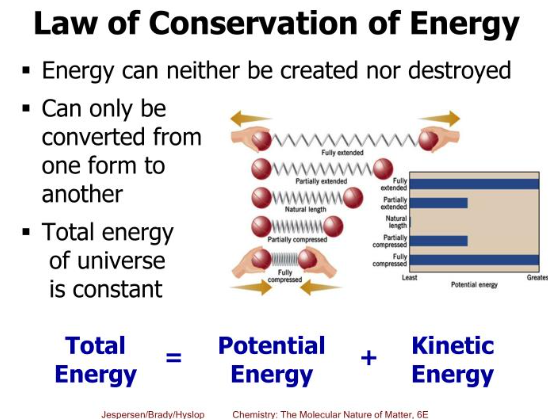
Law of Conservation of energy
The Law of Conservation of Energy is a fundamental principle that governs the behavior of energy in various systems. By exploring different scenarios, we can clearly observe how energy is transformed or transferred without being created or destroyed. Understanding and adhering to this law have significant implications for energy conservation, sustainability, and the development of efficient technologies. By embracing the principles of energy conservation, we can contribute to a more sustainable and responsible use of energy in our daily lives and beyond.