Orbital Diagram for Sulfur: Understanding the Electron Configuration
Sulfur is an essential chemical element with the atomic number 16 and the symbol S on the periodic table. To better understand the electron configuration of sulfur, we can examine its orbital diagram. In this article, we will delve into the orbital diagram for sulfur, exploring its electron arrangement and shedding light on its chemical behavior and properties.
1. Understanding Electron Configuration
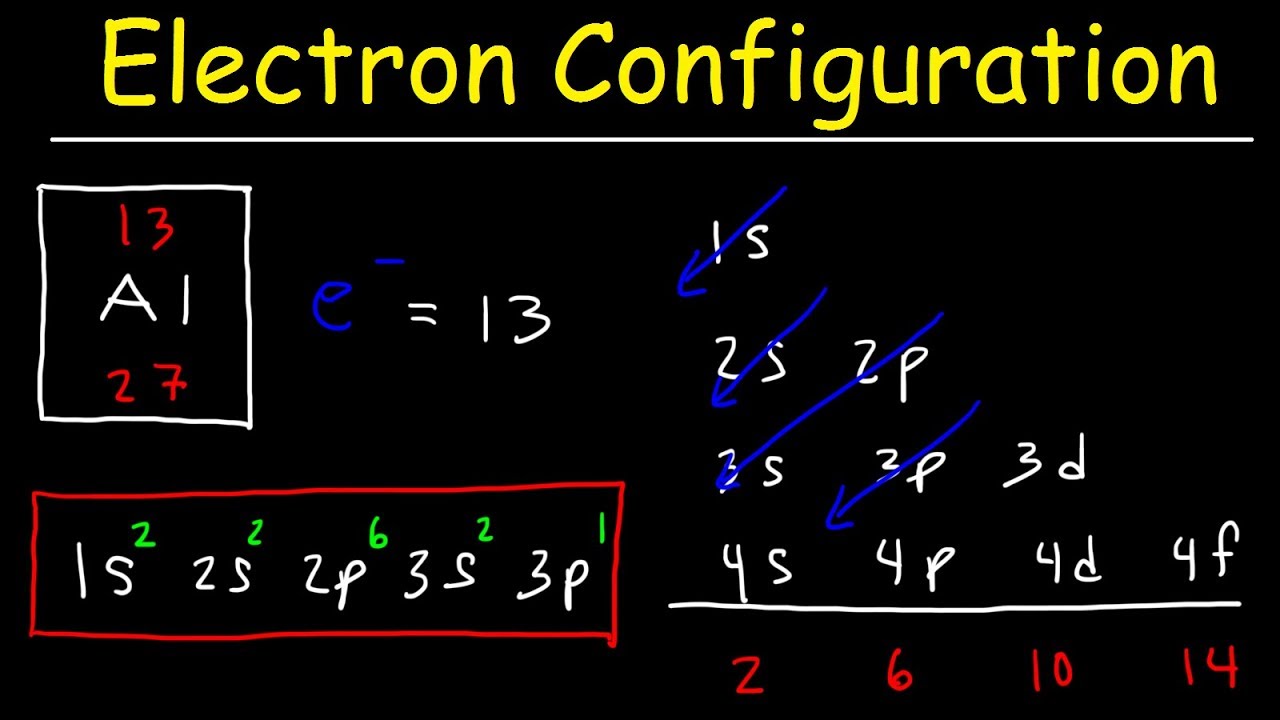
Electron Configuration
Electron configuration refers to the distribution of electrons in an atom's energy levels or orbitals. It provides valuable information about an element's chemical properties and its reactivity with other elements.
The orbital diagram is a visual representation of the electron configuration, showing the specific arrangement of electrons in the atom's orbitals.
2. Sulfur's Electron Configuration
The electron configuration of sulfur is 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^4. This configuration can be further represented using the orbital diagram, which illustrates the arrangement of electrons in each orbital.
3. Orbital Diagram for Sulfur
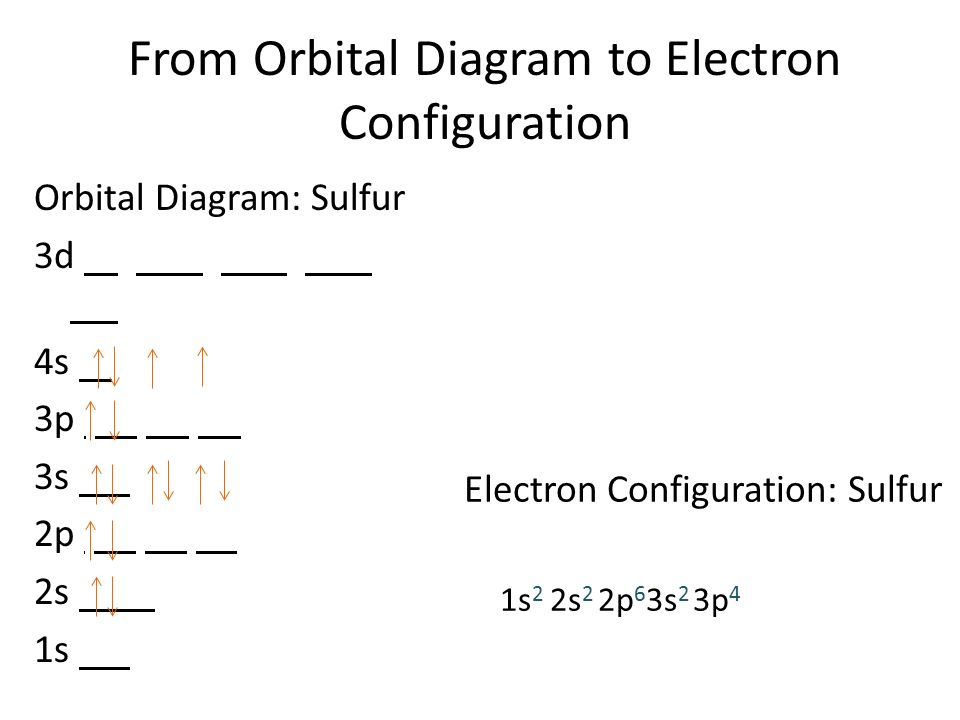
Orbital Diagram for Sulfur
To understand the orbital diagram for sulfur, we need to consider the sequence of orbitals and the number of electrons in each orbital. The orbitals are represented by boxes, with the electrons depicted as arrows indicating their spin.
The first energy level, or the 1s orbital, can accommodate a maximum of two electrons. In the orbital diagram for sulfur, two arrows are placed in the 1s box, representing the two electrons present in this orbital.
The second energy level consists of the 2s and 2p orbitals. The 2s orbital can hold up to two electrons, and in the orbital diagram, two arrows are placed in the 2s box. The 2p orbital has three separate orbitals (2p_x, 2p_y, and 2p_z), each capable of holding two electrons. Therefore, a total of six arrows are distributed across the 2p boxes.
The third energy level includes the 3s and 3p orbitals. Similar to the 2s orbital, the 3s orbital can hold a maximum of two electrons, represented by two arrows in the 3s box. The 3p orbital, with its three separate orbitals (3p_x, 3p_y, and 3p_z), can accommodate a total of six electrons. Hence, six arrows are distributed across the 3p boxes.
4. Chemical Behavior of Sulfur
Sulfur's electron configuration influences its chemical behavior. With six valence electrons in its outermost energy level (3s^2 3p^4), sulfur tends to form two covalent bonds by sharing electrons with other elements.
It can also gain two electrons to achieve a stable noble gas configuration, similar to the nearest noble gas, argon (1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^6). Sulfur commonly forms compounds with elements like oxygen, hydrogen, and metals.
5. Properties of Sulfur
Sulfur is known for its distinctive physical and chemical properties. It is a yellow, brittle solid at room temperature, with a characteristic odor. Sulfur is insoluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents.
It is a nonmetal and exhibits both metallic and nonmetallic properties, making it a versatile element with diverse applications.
The orbital diagram for sulfur provides valuable insights into its electron configuration, shedding light on its chemical behavior and properties. With an electron configuration of 1s^2 2s^2 2p^6 3s^2 3p^4, sulfur possesses six valence electrons that play a crucial role in its reactivity and bonding with other elements. Understanding the orbital diagram allows us to comprehend sulfur's electron arrangement, providing a foundation for further exploration of its chemical interactions and applications in various fields.