Which Pure Substance Can Be Classified as an Element?
In the field of chemistry, pure substances play a crucial role in understanding the fundamental building blocks of matter. Among these pure substances, elements hold a significant place. This article aims to explore the concept of elements and shed light on which pure substances can be classified as elements. By providing a comprehensive understanding of elements and their characteristics, readers will gain insight into the fundamental components of matter.
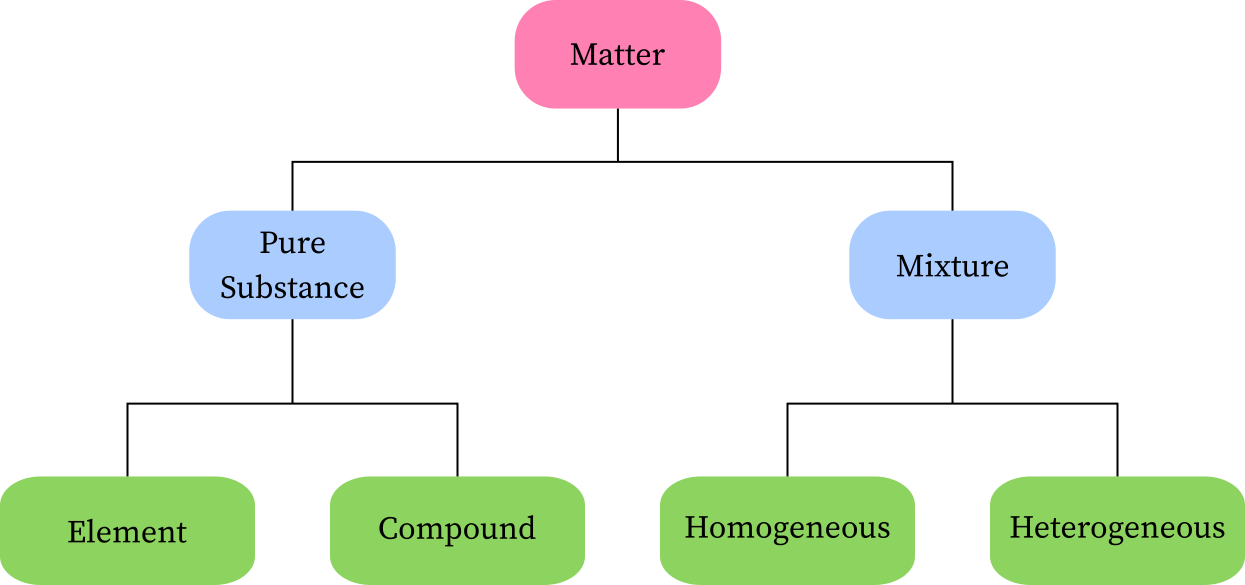
Classification of Matter
1. Understanding Pure Substances:
Before delving into the classification of elements, it is important to comprehend the concept of pure substances.
Pure substances are materials that are made up of a single type of particle or molecule.
They possess consistent and predictable properties throughout the substance. Pure substances can be categorized into two types: elements and compounds.
2. Definition and Characteristics of Elements:
An element is a pure substance that consists of only one type of atom. It is the simplest form of matter and cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means.
Elements are characterized by their unique atomic number, which represents the number of protons in the nucleus of their atoms. They also possess specific physical and chemical properties that distinguish them from other elements.
3. The Periodic Table:
The classification of elements is organized in the Periodic Table.
This table arranges elements based on their atomic number and groups them into periods (horizontal rows) and groups (vertical columns).
The Periodic Table provides a systematic representation of all known elements, showcasing their properties, atomic mass, and electron configurations.
4. Identification of Elements:
To determine which pure substances can be classified as elements, scientists use various techniques.
One crucial method is spectroscopy, which analyzes the interaction of matter with electromagnetic radiation.
Spectroscopic techniques enable the identification and quantification of elements present in a sample based on the characteristic wavelengths of light they absorb or emit.
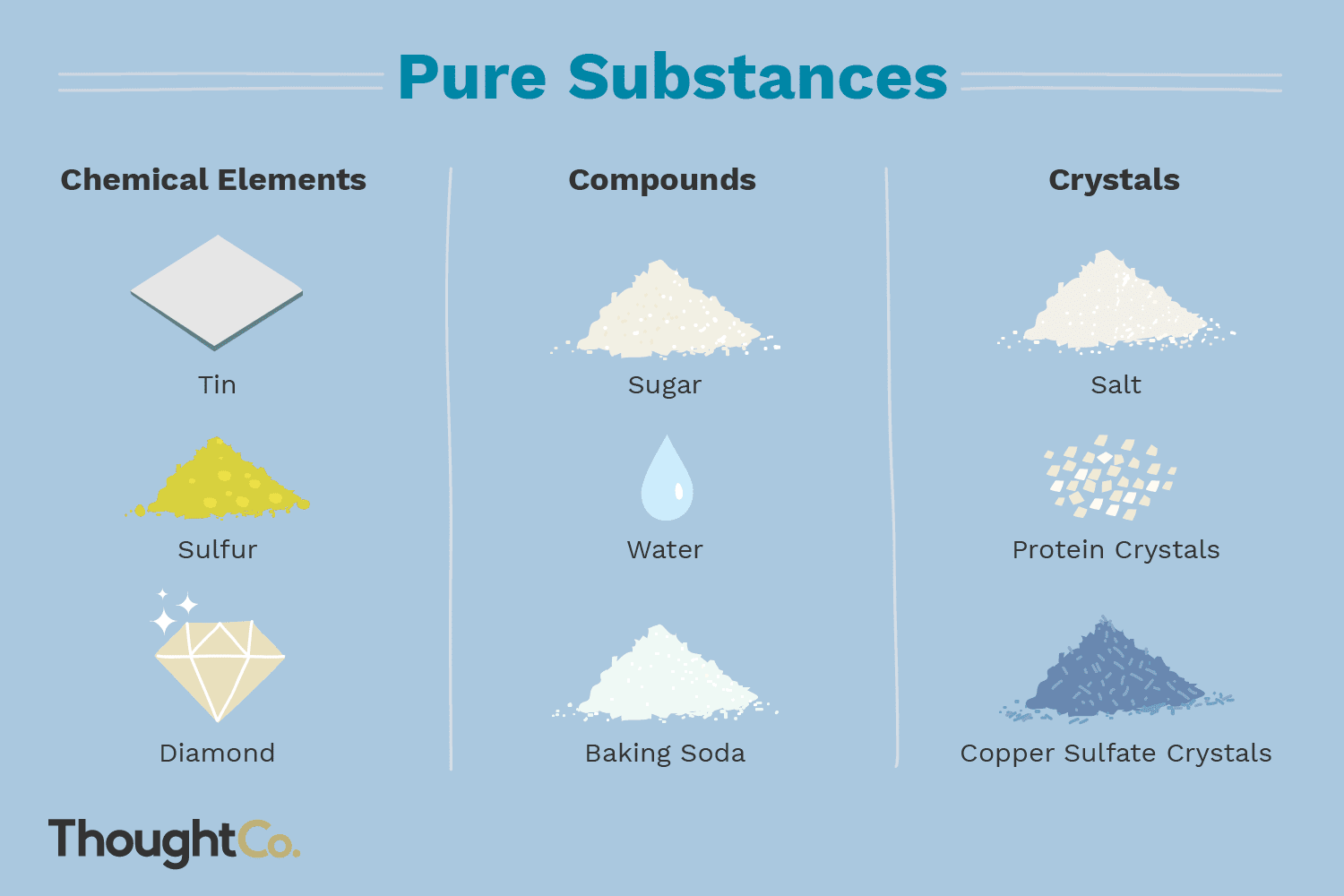
Pure substances
5. Examples of Elements:
A wide range of pure substances can be classified as elements. Some commonly known elements include oxygen, hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen, gold, silver, iron, and copper.
These elements have distinct properties and are vital for various chemical reactions, biological processes, and industrial applications.
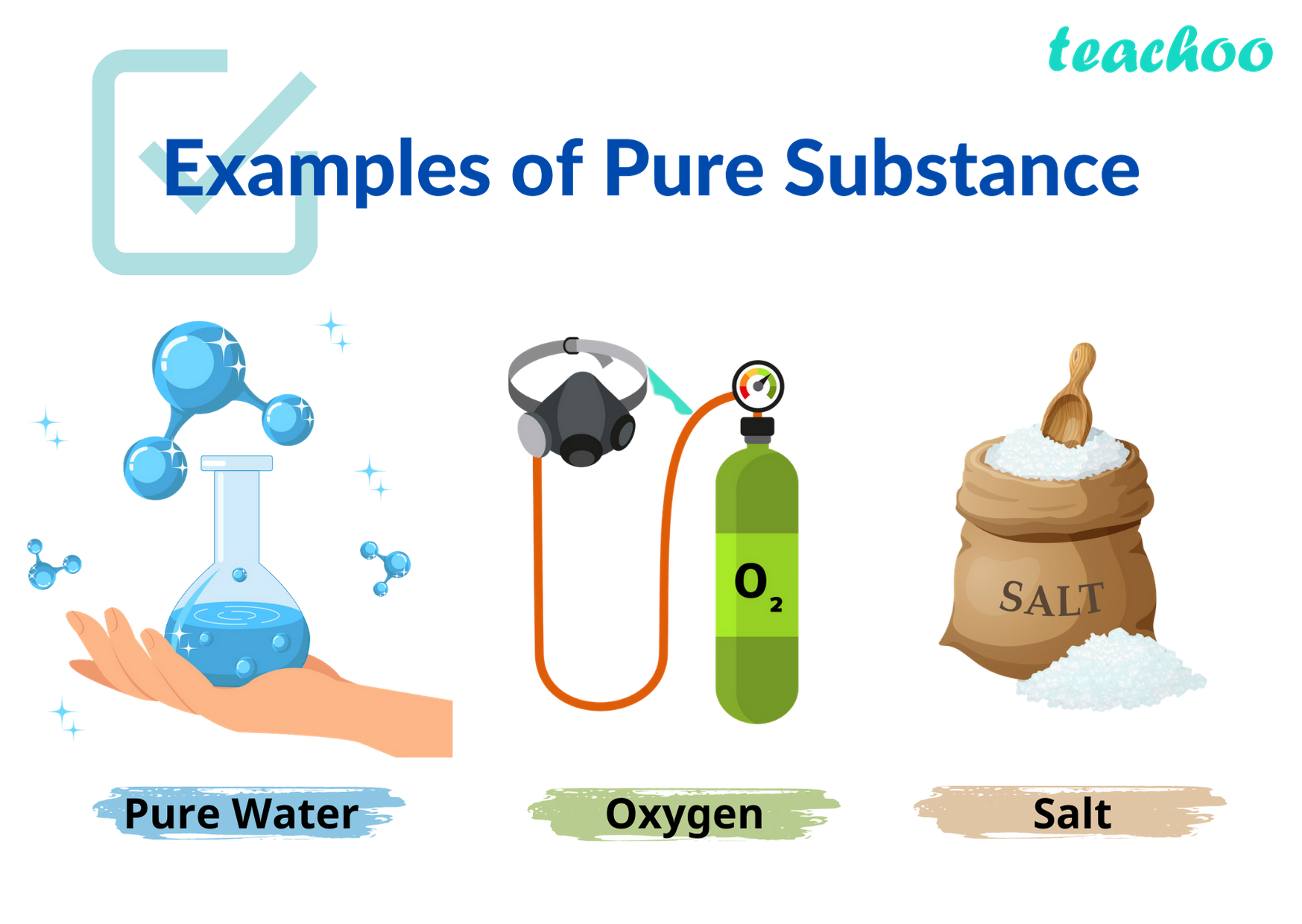
Examples of Elements
6. Allotropes and Isotopes:
Elements can exist in different forms known as allotropes. Allotropes are different structural arrangements of atoms within the same element, resulting in varying physical and chemical properties.
For example, carbon can exist as diamond, graphite, or fullerene, each having distinct properties. Isotopes, on the other hand, are variants of an element that have the same number of protons but differ in the number of neutrons.
7. Importance of Elements:
Elements are the fundamental building blocks of matter and have immense importance in various fields.
They are essential for understanding chemical reactions, formulating medicines, developing materials, generating energy, and supporting life processes.
Elements also contribute significantly to the fields of physics, biology, geology, and environmental science.
In conclusion, elements are pure substances that consist of a single type of atom and cannot be further broken down by chemical means. The Periodic Table serves as a comprehensive classification system for elements.
Through spectroscopic techniques, scientists identify and analyze elements based on their unique properties. Elements play a vital role in various scientific and practical applications, making them the key components of our world.
Understanding the nature and characteristics of elements is crucial for gaining insight into the fundamental aspects of matter.