Astronomical Distances: How Many Light Years Is Mars from Earth?
The universe is a vast expanse of celestial wonders that have fascinated humanity for centuries. Among these wonders, Mars—the fourth planet from the Sun—holds a special place as a neighboring world that has captured our curiosity. One common question that arises in discussions of space is "how many light years is Mars from Earth?" In this article, we'll delve into the topic of interplanetary distances, demystifying the concept of light years and providing a clear understanding of the distance between Earth and Mars.
1. Introduction to Mars: The Red Planet

Mars
Before we explore the specifics of interplanetary distances, let's introduce Mars.
Often referred to as the "Red Planet" due to its distinctive reddish appearance, Mars has long been a subject of scientific research, space exploration, and speculation about the potential for life beyond Earth.
2. The Measure of Distances: Light Years
To understand the distance between Earth and Mars, we need to grasp the concept of a light year.
A light year is a unit of measurement used to denote the distance light travels in a year—a staggering 5.88 trillion miles (9.46 trillion kilometers).
3. Earth and Mars: A Comparative Overview
Earth and Mars are two neighboring planets in our solar system, with Earth being the third planet from the Sun and Mars being the fourth.
While both planets share certain similarities, such as a day-night cycle and an atmosphere, they also have distinct characteristics that make each world unique.
4. The Myth of Light Years: The Proximity of Mars
Contrary to popular belief, Mars is not measured in light years from Earth.
The confusion arises from the term "light year" itself, which pertains to interstellar distances. In reality, Mars is relatively close to Earth in astronomical terms.
5. The Astronomical Unit (AU): A More Appropriate Measure
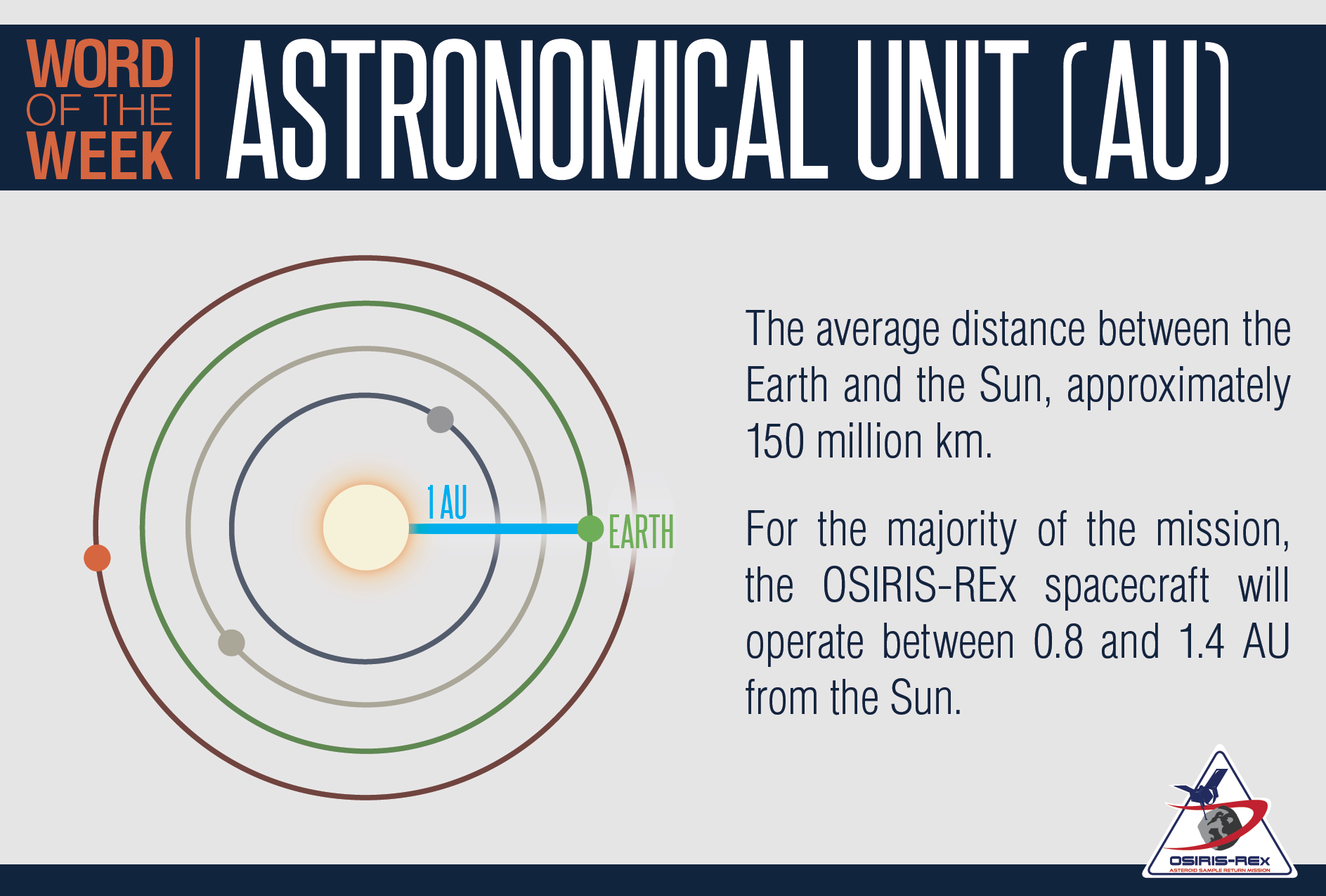
Astronomical Unit
When discussing distances within our solar system, astronomers often use a unit known as the astronomical unit (AU).
One astronomical unit is the average distance between Earth and the Sun—about 93 million miles (150 million kilometers).
6. The Distance from Earth to Mars: A Matter of Proximity
Mars orbits the Sun at an average distance of about 1.52 astronomical units. This means that at its closest point (opposition), Mars is approximately 0.52 astronomical units away from Earth, or around 48.5 million miles (78 million kilometers).
7. Mars Opposition: A Favorable Alignment
Mars opposition occurs when Earth and Mars are positioned in a way that Mars appears on the opposite side of the sky from the Sun.
During this alignment, Mars is at its closest approach to Earth, making it an ideal time for observing the planet through telescopes.
8. Space Travel to Mars: Navigating the Distance
The proximity of Mars to Earth is a factor that has influenced space exploration efforts.
Missions to Mars are carefully planned to take advantage of favorable oppositions, reducing travel time and fuel requirements.
9. The Importance of Measurement: Advancing Astronomy
Accurate measurement of distances within our solar system and beyond is crucial for advancing our understanding of the cosmos.
Whether studying the orbits of planets, predicting celestial events, or planning space missions, precise measurements shape the field of astronomy.
In conclusion, while the question "how many light years is Mars from Earth?" may be a common query, the answer lies in the realm of astronomical units rather than light years. Mars and Earth share a relatively close proximity in our solar system, with Mars being reachable through space missions that take advantage of optimal opposition alignments. As we continue to explore the universe and uncover its mysteries, understanding the distances between celestial bodies is essential for enriching our knowledge of the cosmos and shaping the future of space exploration.