Understanding Glycerol + Cu(OH)2 Reaction: Chemical Properties and Applications
Chemical reactions are fundamental to the field of chemistry, and understanding them is crucial for various applications. In this article, we will explore the reaction between glycerol (also known as glycerin) and copper(II) hydroxide (Cu(OH)2). We will delve into the chemical properties of glycerol, the role of copper(II) hydroxide, and the potential applications of this reaction.

Glixerol + CuOH2
1. Introduction to Glycerol
a. Glycerol Overview: Glycerol is a colorless, odorless, and sweet-tasting organic compound. It is a trihydric alcohol with the chemical formula C3H8O3.
b. Versatility: Glycerol has numerous applications, including its use as a solvent, sweetener, and in the production of cosmetics, pharmaceuticals, and food products.
2. Copper(II) Hydroxide: An Overview
a. Copper(II) Hydroxide Introduction: Copper(II) hydroxide (Cu(OH)2) is a chemical compound composed of copper ions and hydroxide ions. It is typically a light blue solid.
b. Chemical Properties: Copper(II) hydroxide is used in agriculture as a fungicide and has other applications in the synthesis of copper compounds.
3. The Glycerol + Cu(OH)2 Reaction
a. Reaction Description: When glycerol and copper(II) hydroxide are combined, they undergo a chemical reaction.
b. Products Formed: The reaction between glycerol and copper(II) hydroxide typically forms copper(II) glycerolate, a complex coordination compound.
4. Chemical Equation and Balancing
Balanced Equation: The balanced chemical equation for the reaction between glycerol and copper(II) hydroxide is:
C3H8O3 + Cu(OH)2 → Cu(C3H7O3)2 + 2H2O
5. Applications and Uses
a. Role in Agriculture: Copper(II) glycerolate, formed in this reaction, is utilized in agriculture as a copper source in fungicides and bactericides.
b. Coordination Chemistry: This reaction showcases coordination chemistry principles, where glycerol acts as a ligand coordinating to the central copper ion.
6. Safety Considerations
a. Handling Precautions: When working with chemicals like copper(II) hydroxide, it is essential to follow safety guidelines, including wearing appropriate protective gear and working in a well-ventilated area.
b. Disposal: Proper disposal methods for any leftover chemicals should be followed in accordance with local regulations.
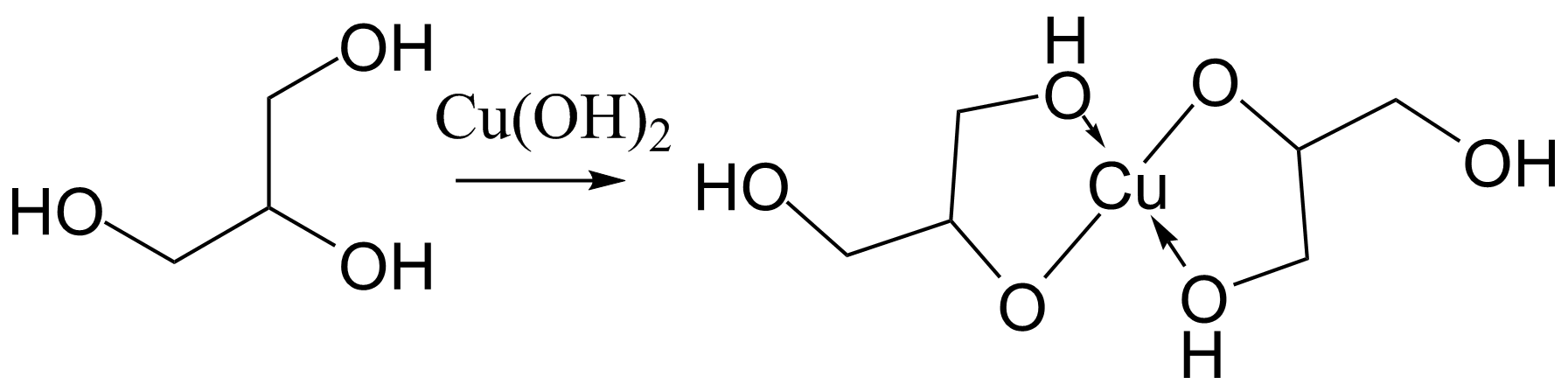
Glixerol + CuOH2
The reaction between glycerol and copper(II) hydroxide serves as a notable example of chemical reactions with practical applications. Understanding the products and principles behind this reaction is valuable in fields like agriculture and coordination chemistry. As with any chemical reaction, safety precautions should be observed when working with these substances to ensure safe experimentation and application.