Which Natural Resource is Not Abundant in Africa?
Africa is a continent known for its rich and diverse natural resources, including minerals, oil, gas, and agricultural products. However, not all resources are equally abundant across the continent. In this article, we will explore which natural resource is not commonly found in abundance in Africa. Understanding the availability of resources can shed light on the economic potential and challenges faced by African countries.

Top Afirican countries with the most abundant natural resources
I. Abundant Natural Resources in Africa:
Africa is blessed with a wealth of natural resources that have played a significant role in shaping the continent's economy. Here are some of the abundant natural resources found in Africa:
A. Minerals and Metals:
Africa is renowned for its mineral wealth, and several countries on the continent are major producers of various minerals and metals. Some of the abundant resources include:
1. Gold: African countries such as South Africa, Ghana, and Tanzania are known for their gold production, making Africa a significant contributor to the global gold supply.
2. Diamonds: Countries like Botswana, Angola, and the Democratic Republic of Congo have rich diamond deposits, making Africa a leading producer of diamonds.
3. Copper: Zambia and the Democratic Republic of Congo are major copper producers, contributing significantly to the global copper supply.
4. Platinum: South Africa holds the majority of the world's platinum reserves and is the largest producer of this precious metal.
5. Iron ore: African countries such as South Africa, Mauritania, and Algeria have substantial iron ore deposits, supporting the global steel industry.
B. Oil and Gas:
Africa is home to significant oil and gas reserves, making it an important player in the global energy market. Key resources include:
1. Crude oil: Countries like Nigeria, Angola, and Algeria are major oil producers, contributing to Africa's oil-rich reputation.
2. Natural gas: African countries such as Nigeria, Mozambique, and Algeria have abundant natural gas reserves, supporting domestic energy needs and exports.
3. Petroleum products: Africa's oil refineries produce various petroleum products, including gasoline, diesel, and jet fuel, supporting transportation and industrial sectors.
C. Agricultural Products:
Agriculture is a vital sector in Africa, and the continent boasts abundant agricultural resources. Some of the notable agricultural products include:
1. Cocoa: West African countries, particularly Ivory Coast and Ghana, are leading cocoa producers, supplying a significant portion of the world's cocoa beans.
2. Coffee: Ethiopia, Uganda, and Kenya are known for their high-quality coffee production, contributing to the global coffee market.
3. Tea: Countries like Kenya, Malawi, and Tanzania have extensive tea plantations and are major exporters of tea.
4. Palm oil: Nigeria, Ghana, and Côte d'Ivoire are significant palm oil producers, contributing to the global demand for this versatile oil.
5. Rubber: African countries such as Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire, and Nigeria have vast rubber plantations, supporting various industries.
6. Timber: The continent is rich in forests, and countries like Cameroon, Democratic Republic of Congo, and Gabon are known for their timber production.
II. Scarce Natural Resources in Africa:
While Africa is abundant in many natural resources, there are also certain resources that are relatively scarce. Here are some examples:
A. Freshwater:
Access to clean freshwater is a significant challenge in many parts of Africa. Factors such as limited rainfall, population growth, and inadequate infrastructure contribute to water scarcity in certain regions.
1. Water scarcity challenges in certain regions of Africa: Some regions, such as the Sahel, experience prolonged periods of drought, resulting in water scarcity and its associated consequences.
2. Limited availability of freshwater resources: The uneven distribution of water resources across the continent leads to disparities in access to clean and safe water for drinking, agriculture, and sanitation purposes.
3. Importance of water management and conservation efforts: Efficient water management practices, such as rainwater harvesting, water recycling, and the development of irrigation systems, play a crucial role in addressing water scarcity challenges.
B. Natural Gas Reserves:
Although Africa has significant natural gas reserves, it is not as abundant as other continents such as North America and the Middle East. Factors such as limited exploration, infrastructure constraints, and political instability have impacted the development of natural gas resources in certain regions.
1. Overview of natural gas reserves in Africa: While Africa holds substantial natural gas reserves, the exploitation and utilization of these resources vary across countries.
2. Comparison to other continents with larger reserves: Africa's natural gas reserves are relatively smaller compared to regions like North America, which possesses abundant shale gas reserves, and the Middle East, which is known for its vast conventional gas reserves.
3. Potential for further exploration and development: Despite the challenges, there is still untapped potential for discovering and developing additional natural gas reserves in Africa, which can contribute to regional energy security and economic growth.
C. Nuclear Energy:
Nuclear energy is a scarce resource in Africa, with only a few countries currently utilizing this form of power generation. Factors such as high upfront costs, technical expertise requirements, safety concerns, and public perception have limited the development of nuclear energy on the continent.
1. Limited utilization of nuclear energy in Africa: Only a handful of African countries, including South Africa, Egypt, and Nigeria, have operational nuclear power plants or plans for future development.
2. Challenges and considerations related to nuclear power: The development of nuclear energy requires significant investment, specialized infrastructure, skilled workforce, and stringent safety measures, which pose challenges for many African countries.
3. Focus on renewable energy sources instead: To meet their growing energy needs, many African countries are shifting their focus toward renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and hydroelectric power, which are more accessible, cost-effective, and environmentally sustainable.
III. Economic Implications and Challenges:
The availability or scarcity of natural resources in Africa has significant economic implications and presents certain challenges for the continent's development. Here are some key points:
A. Impact on Energy Sector:
The abundance or scarcity of energy resources influences the energy mix and energy security of African countries.
1. Reliance on imported natural gas and its effects on energy security: Countries with limited natural gas reserves often rely on imports, which can lead to energy security concerns and vulnerability to price fluctuations.
2. Strategies to diversify energy sources and reduce dependence: To address energy challenges, many African nations are implementing strategies to diversify their energy sources, promote renewable energy, and reduce dependence on a single resource.
B. Water Scarcity and Agriculture:
Water scarcity has significant implications for agricultural production and food security in Africa.
1. Effect of limited freshwater resources on agriculture: Water scarcity affects irrigation, crop production, and livestock farming, impacting food production and rural livelihoods.
2. Importance of water-efficient farming practices and irrigation techniques: Efficient water management techniques such as drip irrigation, water recycling, and conservation agriculture are crucial for optimizing water usage and increasing agricultural productivity.
C. Opportunities for Development:
Despite the challenges associated with scarce resources, there are opportunities for development and sustainable practices in Africa.
1. Exploration of alternative energy sources and technologies: Investing in renewable energy sources such as solar, wind, and geothermal power can help diversify the energy mix and promote sustainable development.
2. Potential for water conservation initiatives and sustainable agriculture: Implementing water conservation practices, improving water infrastructure, and promoting sustainable farming techniques can enhance water availability for agriculture and mitigate the impact of water scarcity.
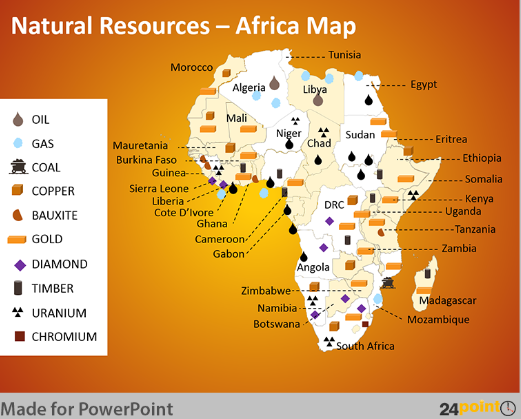
Natural Resources - Africa map
Africa is a continent rich in natural resources, providing valuable minerals, oil, gas, and agricultural products to the global market. However, certain resources are relatively scarce, such as freshwater, abundant natural gas reserves, and nuclear energy. Understanding the availability and challenges associated with these resources is crucial for sustainable development, addressing energy security concerns, promoting water conservation, and exploring alternative solutions. By adopting innovative strategies, Africa can harness its abundant resources while mitigating the impact of scarce resources, paving the way for economic growth, social development, and environmental sustainability.