How Many Protons Does Lithium Have? Exploring the Atomic Structure of Lithium
The world of chemistry is a fascinating realm filled with elements that form the foundation of matter. One such element is lithium, a versatile and essential component found in various applications. A fundamental question often arises: How many protons does lithium have? In this article, we delve into the atomic structure of lithium, uncovering its proton count and shedding light on the significance of this element in the realm of science and technology.
1. The Building Blocks of Matter: Elements and Protons
Elements and Protons
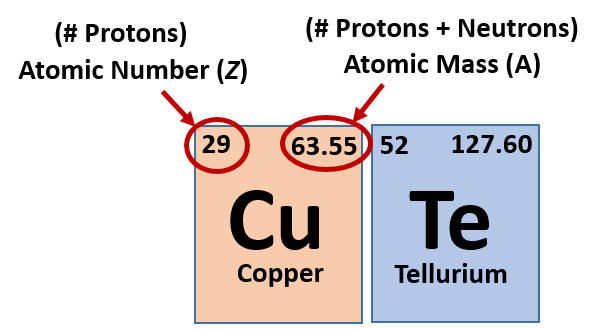
1.1 The Periodic Table:
The periodic table categorizes elements based on their atomic number, which corresponds to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom.
1.2 Protons: The Atomic Identity:
Protons are positively charged subatomic particles found in the nucleus of an atom. The number of protons uniquely defines the element and its properties.
2. Lithium's Atomic Structure
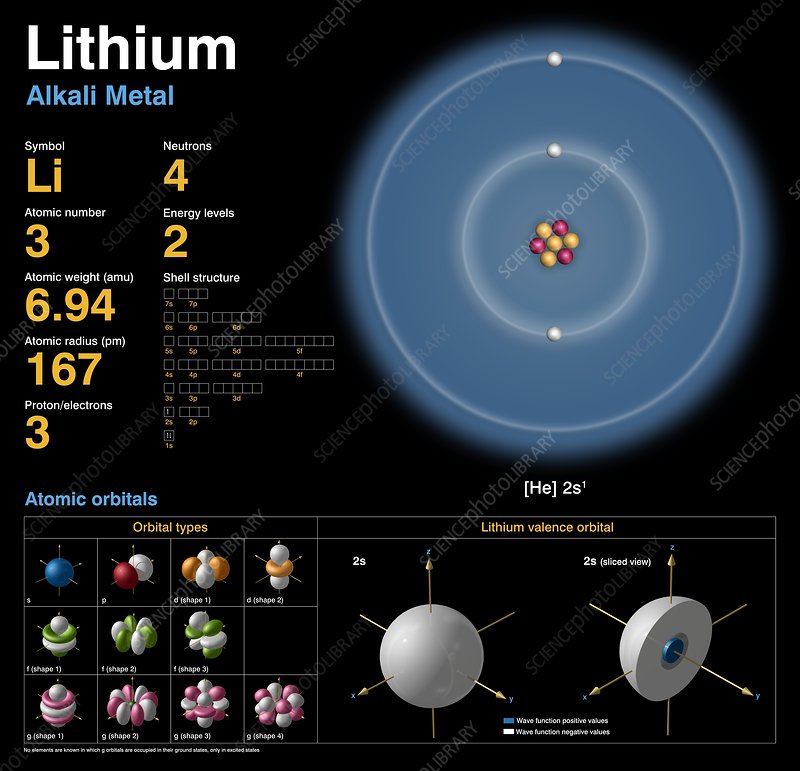
2.1 Element Symbol:
Lithium is represented by the chemical symbol "Li" on the periodic table, signifying its unique place among the elements.
2.2 Atomic Number:
The atomic number of an element corresponds to the number of protons in its nucleus. In the case of lithium, its atomic number is 3, indicating the presence of 3 protons.
3. Significance of Lithium's Proton Count
Lithium's Proton
3.1 Elemental Properties:
The number of protons in an element's nucleus directly influences its chemical and physical properties, including its behavior in reactions, bonding, and more.
3.2 Reactivity and Bonding:
Lithium's proton count of 3 contributes to its reactivity, making it highly reactive and capable of forming various compounds through chemical bonding.
4. Lithium's Applications and Uses
4.1 Batteries and Energy Storage:
Lithium-ion batteries have revolutionized portable electronics and renewable energy storage, powering devices from smartphones to electric vehicles.
4.2 Medical and Pharmaceutical Applications:
Lithium compounds are used in psychiatric medications to treat bipolar disorder, showcasing the element's impact on medical advancements.
4.3 Industrial Processes:
Lithium's unique properties make it valuable in industrial processes such as heat-resistant ceramics and glass production.
5. Isotopes and Variations
5.1 Natural Isotopes:
Lithium has two stable isotopes: lithium-6 (Li-6) and lithium-7 (Li-7), with the latter being more abundant.
These isotopes have slightly different properties due to their varying neutron counts.
5.2 Radioactive Isotopes:
Lithium also has radioactive isotopes, including lithium-5 (Li-5), with applications in nuclear research and medical imaging.
6. Exploring the Nucleus: Beyond Protons
6.1 Neutrons and Atomic Mass:
Neutrons, found alongside protons in the nucleus, contribute to an element's atomic mass.
Lithium's isotopes have different neutron counts, affecting their atomic masses.
6.2 Electrons and Atomic Charge:
Electrons, negatively charged particles, orbit the nucleus and balance the atomic charge.
The arrangement of electrons determines an element's chemical behavior.
The question of how many protons lithium has unveils a deeper understanding of this essential element's atomic structure and properties. With an atomic number of 3, lithium's proton count defines its place on the periodic table and its unique characteristics in the realm of chemistry. From its role in energy storage to medical applications and beyond, lithium's versatility showcases the profound impact of its atomic structure on various scientific and technological advancements. By appreciating the relationship between protons, electrons, and neutrons, we gain insight into the intricate world of elements and the fundamental building blocks of our universe.