How Many Protons Does Se Have? - Exploring the Atomic Structure of Selenium
Understanding the atomic structure of elements is crucial for comprehending their properties and behaviors. In this article, we delve into the topic of selenium (Se) and answer the question, "How many protons does Se have?" We will explore the atomic number of selenium, its electron configuration, and its significance in various applications.
I. The Basics of Selenium:
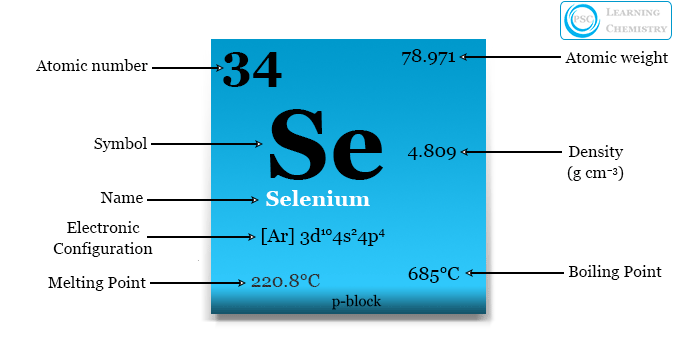
Selenium, represented by the symbol Se, is a chemical element classified as a nonmetal in the periodic table. It is commonly found in nature as a gray crystalline solid and exhibits both photoconductive and photovoltaic properties.
Selenium
II. Atomic Number and Protons:
The atomic number of an element determines the number of protons in its nucleus. For selenium, the atomic number is 34, which indicates that it possesses 34 protons.
Protons of Selenium
III. Electron Configuration:
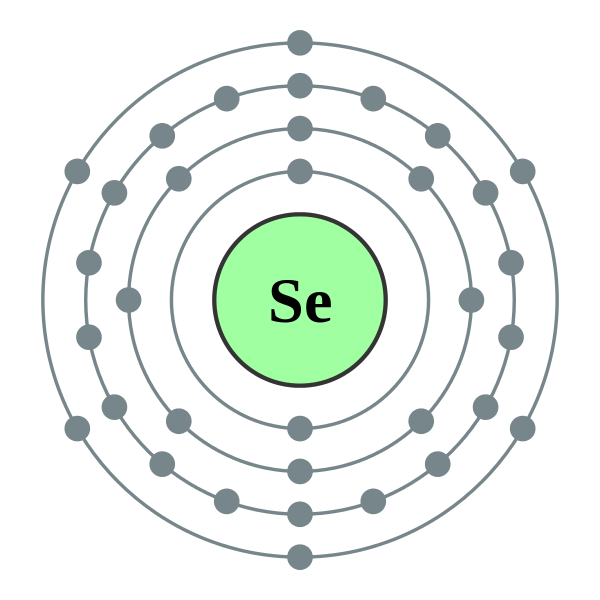
The arrangement of electrons in an atom is known as its electron configuration. In the case of selenium, the electron configuration is 2-8-18-6, following the pattern of filling orbitals based on the Aufbau principle.
IV. Significance of Selenium:
Selenium is essential for various biological functions and has numerous industrial applications. Here are some key areas where selenium plays a crucial role:
1. Health Benefits: Selenium acts as an antioxidant and is believed to have anticancer properties. It also supports the proper functioning of the immune system and thyroid gland.
2. Photovoltaic Cells: Selenium is used in the production of photovoltaic cells, which convert sunlight into electricity. Its unique electrical properties make it an ideal material for this application.
3. Glass Industry: Selenium compounds are employed in the glass industry to decolorize glass and improve its clarity.

Glass Industry
4. Electronics: Selenium rectifiers were commonly used in early electronic devices. Although they have been largely replaced by silicon-based rectifiers, selenium is still utilized in certain specialized electronics.
V. Isotopes of Selenium:
Isotopes are variants of an element with different numbers of neutrons in the nucleus. Selenium has several isotopes, including stable and radioactive ones. Some notable selenium isotopes are ^74Se, ^76Se, ^77Se, and ^82Se.
VI. Selenium in the Environment:
Selenium can be found in soil, water, and air. Its presence in the environment can vary depending on geographical location. Certain regions may have selenium-rich soil, while others may experience selenium deficiency.
VII. Selenium Toxicity:
While selenium is essential in trace amounts, excessive intake can lead to toxicity. Selenium toxicity can occur through the consumption of selenium-rich food sources or exposure to high levels of selenium in the environment. It can have detrimental effects on human health and the ecosystem.
VIII. Conclusion:
In conclusion, selenium, with an atomic number of 34, has 34 protons in its nucleus. Its electron configuration follows the pattern 2-8-18-6. Selenium plays a significant role in various applications, including health benefits, photovoltaic cells, the glass industry, and electronics.
Understanding the atomic structure of selenium provides insights into its properties and applications. However, it is important to be cautious about selenium toxicity and maintain a balanced approach when utilizing this element.