Understanding the Presence and Importance of Melanin in the Human Body
Melanin, a pigment responsible for the coloration of the skin, hair, and eyes, plays a crucial role in the human body. This article aims to explore the significance of melanin and answer the commonly asked question: "How many grams of melanin are present in the human body?" Delving into the science behind melanin, we will discover its diverse functions and shed light on its role in human health.
1. The Nature and Formation of Melanin:
1.1 Melanin Definition and Types:
Melanin is a complex polymer produced by specialized cells called melanocytes. It exists in three main forms: eumelanin, pheomelanin, and neuromelanin.
Eumelanin is responsible for brown and black pigmentation, while pheomelanin accounts for red and yellow pigmentation. Neuromelanin is specific to the brain and central nervous system.
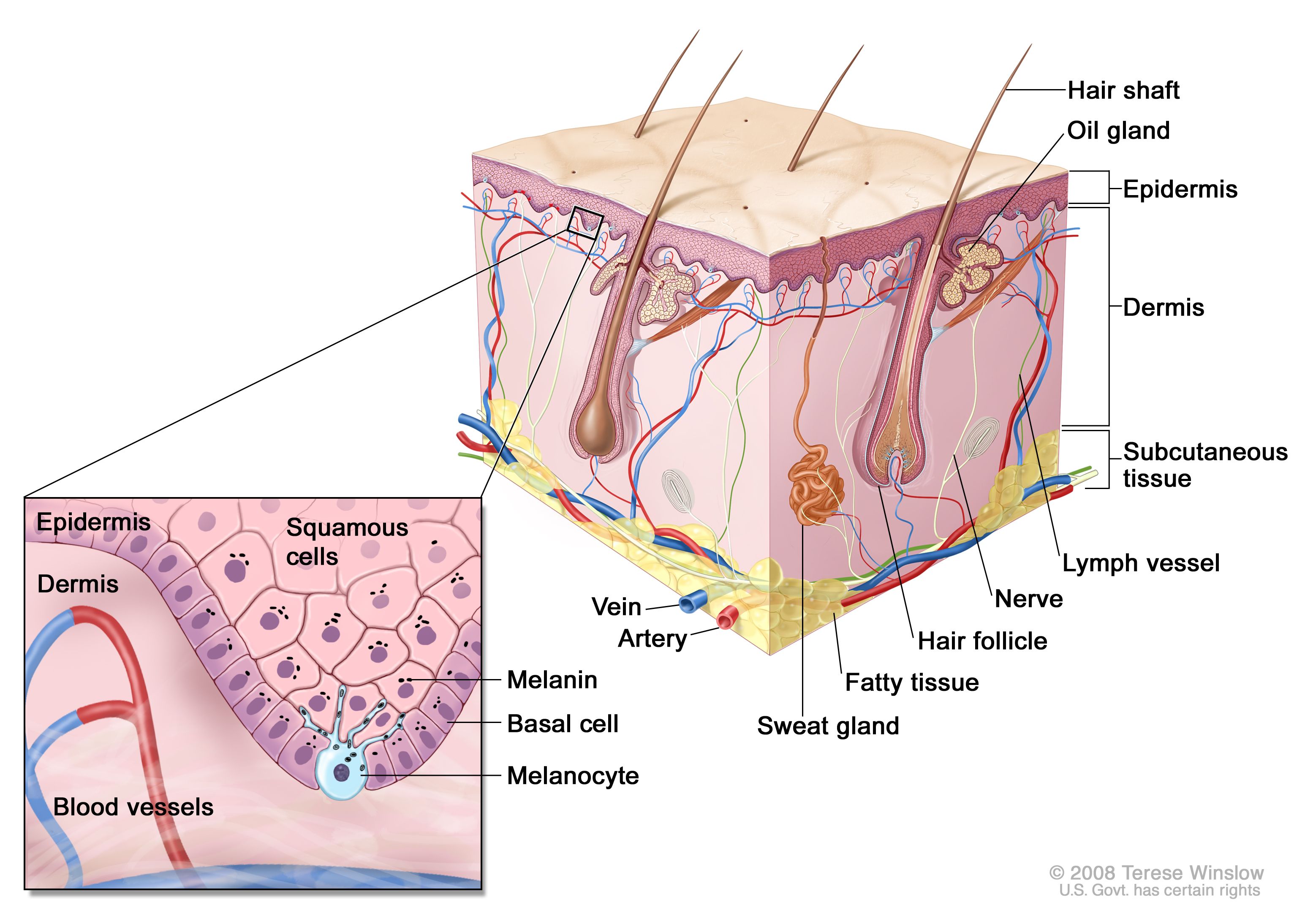
Melanin Production Pathway
1.2 Melanin Production Process:
The synthesis of melanin occurs within melanocytes through a series of biochemical reactions. Tyrosine, an amino acid derived from the diet, serves as the precursor for melanin production.
Enzymes such as tyrosinase, tyrosinase-related protein 1 (TRP-1), and tyrosinase-related protein 2 (TRP-2) play key roles in the conversion of tyrosine to melanin.
2. Functions of Melanin in the Human Body:
2.1 Protection against Ultraviolet (UV) Radiation:
Melanin acts as a natural sunscreen, shielding the skin from harmful UV radiation.
It absorbs UV light, preventing damage to the DNA in skin cells and reducing the risk of skin cancer.
Darker-skinned individuals, who have higher melanin content, exhibit greater natural protection against UV radiation.
2.2 Determination of Skin Color:
The amount and type of melanin present in the skin determine an individual's skin color.
Genetic factors, sun exposure, and environmental factors contribute to the variation in skin pigmentation among different populations.

Essential Tips for Determining Your Skin Tone
2.3 Photoprotection for the Eyes:
Melanin in the eyes helps protect against excessive sunlight, reducing the risk of eye disorders such as cataracts and macular degeneration.
2.4 Hair and Follicle Pigmentation:
Melanin determines the color of hair and provides protection to hair follicles. The absence or decrease of melanin production leads to hair graying or whitening.
2.5 Role in Hearing and Neuroprotection:
Neuromelanin found in the brainstem and substantia nigra is involved in auditory processing and acts as a neuroprotective agent, helping to prevent neurodegenerative diseases like Parkinson's.
3. Quantifying Melanin in the Human Body:
3.1 Difficulty in Measuring Total Melanin Content:
Due to the distributed nature of melanin and variations across individuals, accurately measuring the total amount of melanin in the human body is challenging.
3.2 Estimating Melanin Concentration:
Melanin concentration can be estimated through various methods such as spectrophotometry, reflectance measurements, and skin biopsies.
However, these techniques provide only relative estimates and cannot determine the exact gram value.
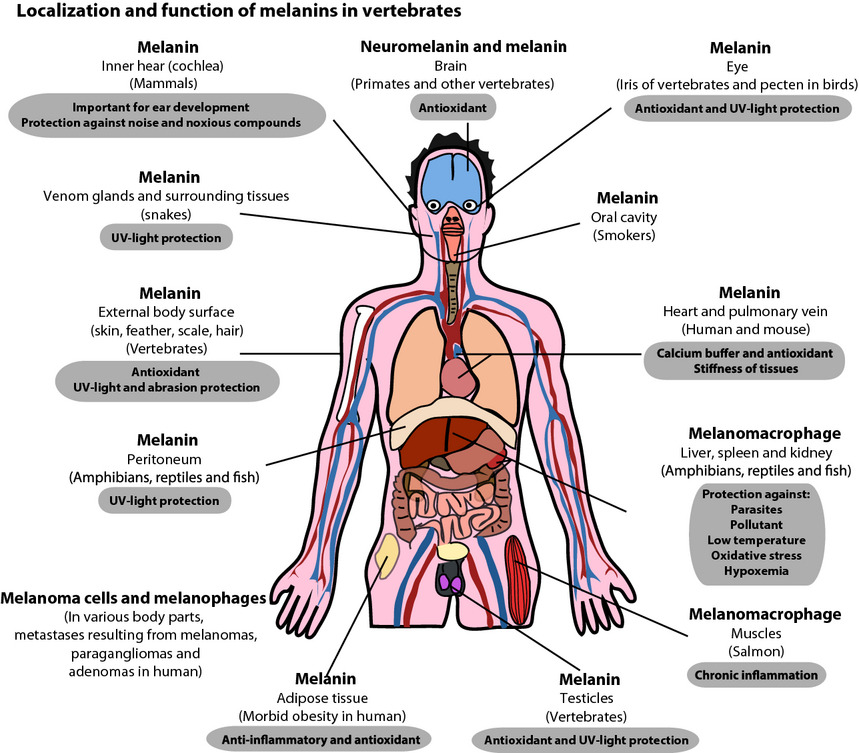
Evolutionary and biomedical consequences of internal melanins
Melanin, a remarkable pigment found in the human body, serves multiple essential functions, including UV protection, determining skin color, and preserving the health of various organs.
While it is difficult to quantify the exact grams of melanin in the human body, its significance cannot be overstated. Understanding the role of melanin enhances our comprehension of human biology and encourages further research in dermatology, ophthalmology, and neurology.