What Is a Natural Propellant? Exploring Nature's Power for Rocketry
When it comes to space exploration and rocketry, propellants play a crucial role in powering spacecraft into the cosmos. While traditional propellants are often synthetic and chemically engineered, there is growing interest in exploring natural alternatives. In this article, we will delve into the concept of natural propellants, discussing what they are, their benefits, and their potential applications in the field of rocketry. Join us as we unravel the power of nature in propelling us to new frontiers.

What is a natural propellant?
1. Understanding Propellants:
Provide an overview of propellants and their role in rocket propulsion. Discuss the components of a typical propellant, including fuel and oxidizer, and how they combine to generate thrust. Highlight the importance of propellant efficiency, stability, and safety in space exploration.
2. Definition and Characteristics of Natural Propellants:
Define what natural propellants are and how they differ from traditional synthetic propellants. Discuss their origins, which can include organic or renewable sources found in nature. Explore the unique characteristics of natural propellants, such as their environmental friendliness, sustainability, and potential for reduced toxicity.
3. Types of Natural Propellants:
Explore various types of natural propellants used or proposed for rocketry. Discuss examples such as liquid propellants derived from biofuels, gaseous propellants like compressed air or steam, and solid propellants made from natural materials. Highlight their advantages, limitations, and current research or implementation.
4. Benefits of Natural Propellants:
Examine the advantages of using natural propellants in rocketry. Discuss their potential for reduced environmental impact, lower carbon emissions, and renewable sourcing. Highlight how natural propellants align with sustainability goals and contribute to a greener approach to space exploration.
5. Challenges and Considerations:
Address the challenges and considerations associated with natural propellants. Discuss factors such as performance efficiency, storage stability, availability of natural resources, and regulatory requirements. Highlight ongoing research and development efforts to overcome these challenges and optimize natural propellant technologies.
6. Applications and Future Prospects:
Discuss the current and potential applications of natural propellants in the field of rocketry. Explore their use in small satellite launches, suborbital flights, and other space missions. Highlight the potential for collaboration between the aerospace industry and environmental organizations to promote the adoption of natural propellant technologies.
7. Safety and Regulations:
Address the safety aspects and regulatory considerations related to natural propellants. Discuss the importance of thorough testing, handling procedures, and adherence to industry standards to ensure the safe use of natural propellants in rocketry.
8. Collaborative Efforts and Research:
Highlight collaborative initiatives and research efforts aimed at advancing natural propellant technologies. Discuss partnerships between space agencies, private companies, and academic institutions to explore and develop new natural propellant solutions. Highlight notable projects or breakthroughs in the field.
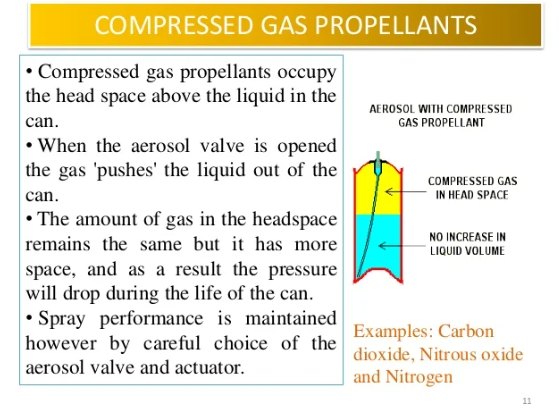
Compressed gas propellants
As we seek more sustainable and environmentally friendly approaches to space exploration, natural propellants offer exciting possibilities. With their renewable sourcing, reduced environmental impact, and potential for increased safety, natural propellants represent a promising avenue for rocketry. While challenges exist, ongoing research and collaborative efforts are paving the way for the development and adoption of natural propellant technologies. By harnessing the power of nature, we can propel ourselves to new horizons while preserving our planet for future generations.