Why Does One Laser Beam Appear Blue While Another Appears Red?
Laser beams have become an integral part of our modern technological advancements, finding applications in various fields ranging from telecommunications to medical procedures. One intriguing aspect of laser beams is their different colors, with some appearing blue and others red. This article aims to explore the factors that contribute to this phenomenon, shedding light on the underlying principles of light and optics.
I. The Nature of Light
To understand why laser beams can have different colors, it is crucial to comprehend the nature of light itself. Light is an electromagnetic wave that travels in a straight line and consists of different wavelengths. Each wavelength corresponds to a specific color in the visible spectrum, ranging from red (longer wavelengths) to violet (shorter wavelengths).
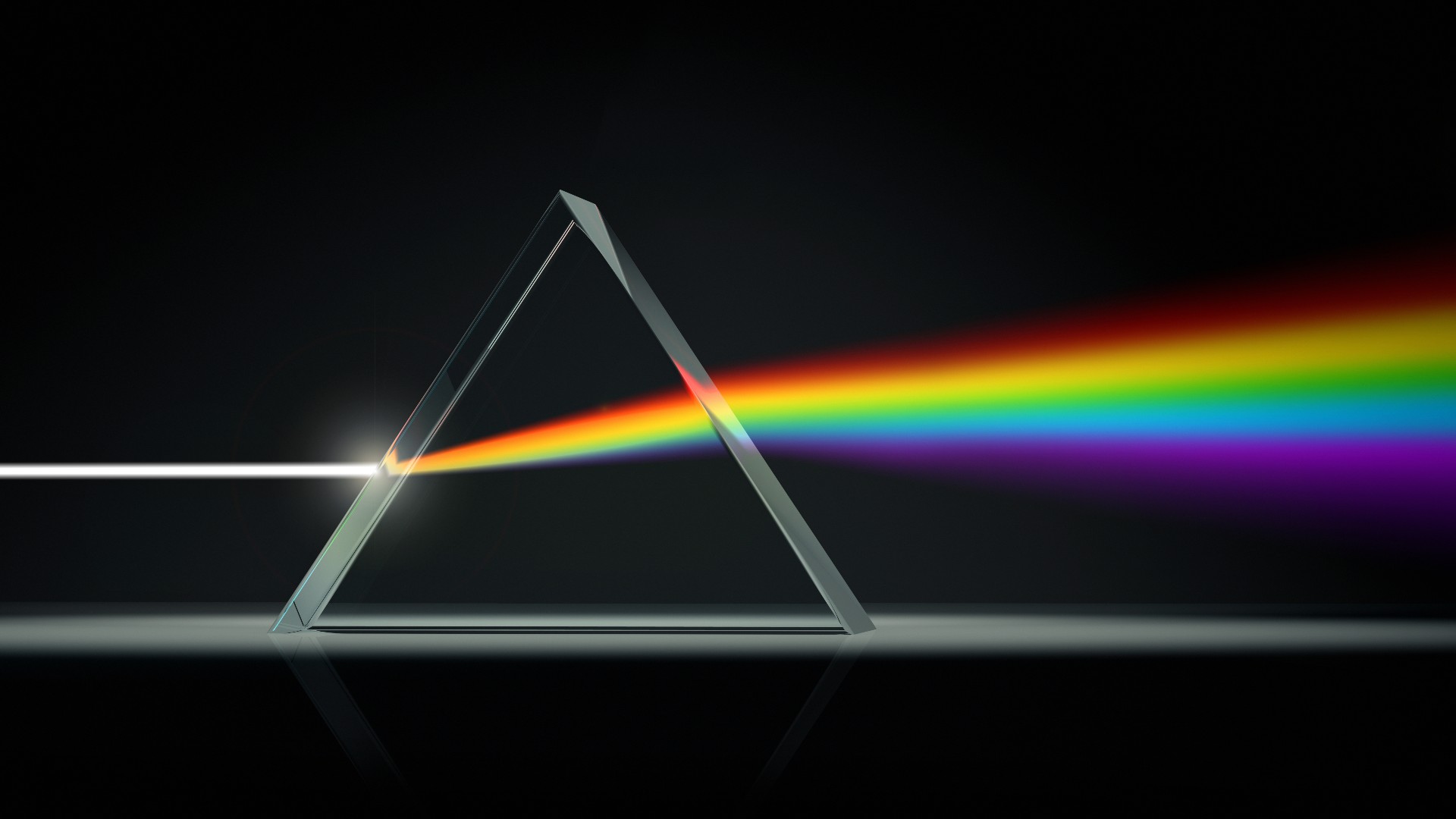
The Nature of Light
II. The Role of Wavelength in Color Perception
The perceived color of light depends on its wavelength. When light interacts with an object, the object absorbs certain wavelengths and reflects others. The reflected light then enters our eyes, where the brain interprets it as color. For instance, an object appears red because it reflects red light while absorbing other wavelengths.
III. Laser Technology
Laser stands for "Light Amplification by Stimulated Emission of Radiation." It is a device that emits a coherent beam of light through a process called stimulated emission. In laser technology, the color of the emitted light is determined by the properties of the medium used to produce the laser beam.
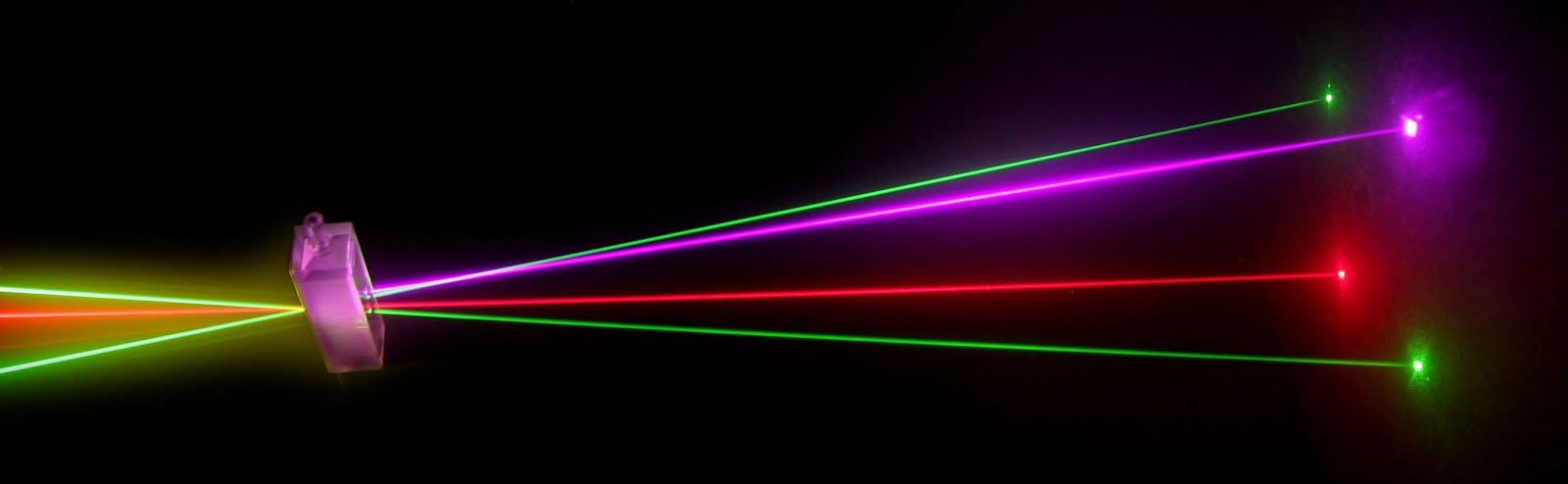

Laser Technology
IV. Factors Influencing Laser Color
1. Energy Levels and Electronic Transitions
Different laser mediums possess unique energy levels and electronic transitions, leading to the emission of specific wavelengths. For example, a laser medium with energy levels that correspond to red light will emit a red laser beam when stimulated.
2. Doping Materials
The process of doping involves introducing impurities into the laser medium to alter its optical properties. By selecting specific dopant materials, engineers can modify the energy levels and electronic transitions within the medium, resulting in lasers with different colors.
3. Stimulated Emission
Stimulated emission is a fundamental process in laser technology. When a photon interacts with an excited atom or molecule, it triggers the emission of a second photon with the same energy, direction, and phase.
This process amplifies the light, resulting in a coherent laser beam. The specific wavelength of the stimulated emission determines the color of the laser beam.
V. Blue Laser Beams
Blue laser beams have gained prominence in recent years due to their unique properties and applications. The development of blue lasers was a significant technological challenge, as the energy levels required for blue light emission are higher compared to other colors.
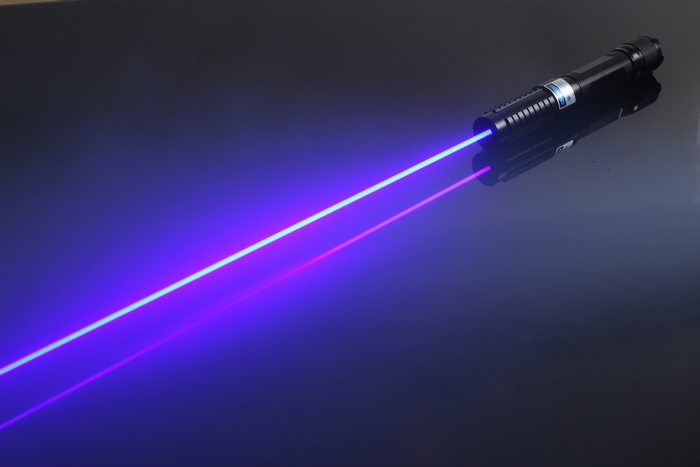

Blue Laser Beams
However, advancements in laser diode technology and the discovery of new materials enabled the creation of efficient blue lasers.
VI. Red Laser Beams
Red laser beams have been widely used in various applications, including laser pointers, barcode scanners, and DVD players. The availability of semiconductor lasers that emit red light, such as the popular red diode lasers, has made red laser technology accessible and cost-effective.
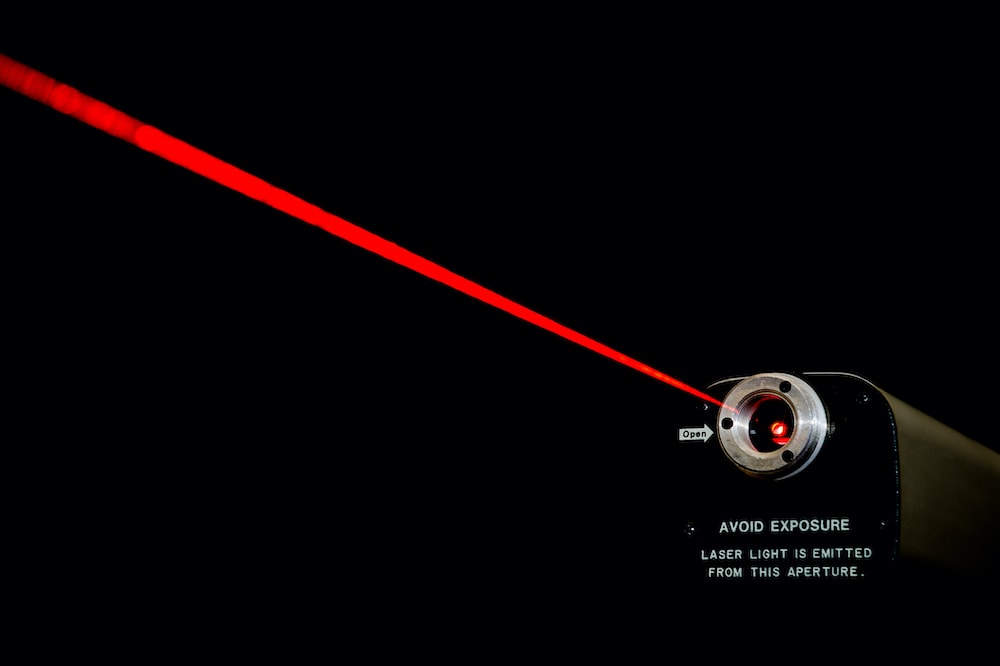
Red Laser Beams
VII. Laser Safety Considerations
Regardless of the color, laser beams should always be handled with caution due to their potential hazards. Different laser classes exist, with each class representing a specific level of danger. Safety precautions, such as wearing appropriate protective eyewear and following safety guidelines, must be strictly adhered to when working with lasers.
VIII. Conclusion
The appearance of laser beams in different colors stems from the specific properties of the laser medium, its energy levels, and the process of stimulated emission.
Understanding the principles behind laser coloration enhances our knowledge of light and optics, facilitating advancements in various fields. By delving deeper into the complexities of laser technology, we can continue to harness the power of lasers for scientific, industrial, and everyday applications.