The Energy Source Behind Wave Formation: Currents, Earthquakes, Sunlight, or Wind?
Waves are a fascinating natural phenomenon found in oceans, lakes, and even smaller bodies of water. Have you ever wondered what energy source is responsible for causing waves to form? In this article, we will explore the different potential sources of energy that contribute to wave formation. We will discuss currents, earthquakes, sunlight, and wind as potential drivers of wave generation, shedding light on their roles and influences in shaping our aquatic environments.
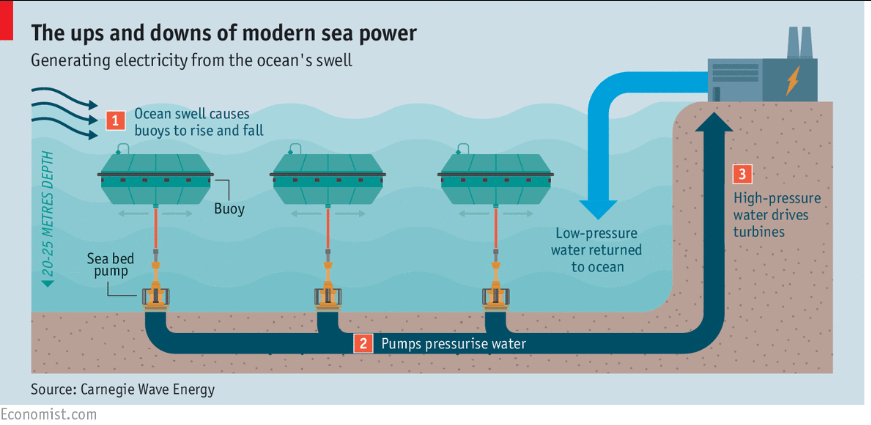
The ups and downs of modern sea power
1. Currents:
A Powerful Force Explain how ocean currents play a significant role in generating waves.
Discuss the movement of water caused by various factors such as tides, temperature gradients, and the rotation of the Earth.
Explore how these currents create disturbances in the water surface, leading to the formation of waves.
2. Earthquakes:
Surprising Wave Generators Highlight the connection between earthquakes and wave formation.
Discuss how seismic activities, particularly those occurring underwater, can create massive disturbances in the water column, resulting in the propagation of waves known as tsunamis.
Explain the mechanisms behind tsunami formation and their potential to cause significant destruction upon reaching coastal areas.
3. Sunlight:
A Subtle Influence Address the role of sunlight in wave formation.
While sunlight may not directly generate waves, it indirectly influences wave patterns through its effects on water temperature and evaporation.
Discuss how temperature differentials caused by sunlight can create surface tension and minor ripples, contributing to the overall wave dynamics.
4. Wind:
The Primary Wave Generator Emphasize the pivotal role of wind in wave formation.
Discuss how wind interacts with the water surface, creating friction and transferring energy to the water.
Explain the concept of wind-generated waves, highlighting how wind speed, duration, and fetch (distance over which wind blows) affect wave height, frequency, and direction.
5. Wave Characteristics and Classification
Provide an overview of the different characteristics and classifications of waves.
Discuss terms such as wavelength, amplitude, period, and wave height, explaining their significance in understanding wave behavior.
Introduce the classification of waves based on their formation mechanisms, including wind waves, tsunamis, and seiche.
6. Wave Energy and Power Generation
Touch upon the concept of wave energy and its potential as a renewable energy source.
Discuss how wave energy converters harness the power of waves to generate electricity.
Highlight the advantages and challenges associated with wave energy technology, including its environmental impact and technological advancements.
7. Coastal Impact and Erosion
Explore the impact of waves on coastal areas, particularly in terms of erosion.
Discuss how wave action, along with other factors such as tides and currents, shapes coastlines and affects the stability of coastal ecosystems.
Address the importance of understanding wave patterns in coastal management and protection.
8. Recreational Activities and Surfing
Examine the recreational aspect of waves, focusing on activities such as surfing.
Discuss the characteristics of waves suitable for surfing, including wave size, shape, and power.
Highlight popular surfing destinations and the culture surrounding this exhilarating sport.
9. Wave Forecasting and Research
Introduce the field of wave forecasting and research.
Discuss the tools and models used to predict wave behavior, including wave buoys, satellites, and computer simulations.
Highlight the importance of accurate wave forecasting for maritime operations, coastal planning, and safety.

Currents earthquakes
Waves are the result of various energy sources, with wind being the primary generator. While currents, earthquakes, and sunlight have their influences on wave formation, wind plays the most significant role in shaping the characteristics and patterns of waves. Understanding the dynamics of wave formation is crucial for coastal management, renewable energy exploration, and recreational activities. Waves truly embody the power and beauty of our aquatic environments.