State Capitals Not Served by Interstates: Exploring America's Road Network
The United States is known for its extensive interstate highway system, connecting cities and states across the country. However, there are a few state capitals that are not served directly by interstates, making their accessibility and transportation infrastructure unique. In this article, we will delve into the state capitals that are not directly connected to the interstate network and discuss the implications of this infrastructure gap.
I. The Importance of Interstates:
Interstate highways play a crucial role in the transportation system of the United States. They provide efficient and convenient routes for both passenger and freight transportation, reducing travel times and promoting economic growth.
Interstate highways
The interstates connect major cities, facilitate interstate commerce, and serve as crucial evacuation routes during emergencies.
II. State Capitals Not Served by Interstates:
While most state capitals enjoy direct interstate access, there are a few exceptions. Let's explore some of these capitals and understand the reasons behind their lack of interstate connectivity:
1. Juneau, Alaska: As the capital of Alaska, Juneau is situated in the southeastern part of the state. Unlike other state capitals, Juneau is not connected to the mainland interstate system due to its geographic isolation. The city is accessible primarily by air and water, making it an exception in terms of interstate connectivity.
2. Honolulu, Hawaii: Hawaii's state capital, Honolulu, is located on the island of Oahu. Similarly to Juneau, Honolulu does not have interstate access due to its island geography. The city relies on local roads and highways for transportation within the island, as well as its extensive public transportation system.
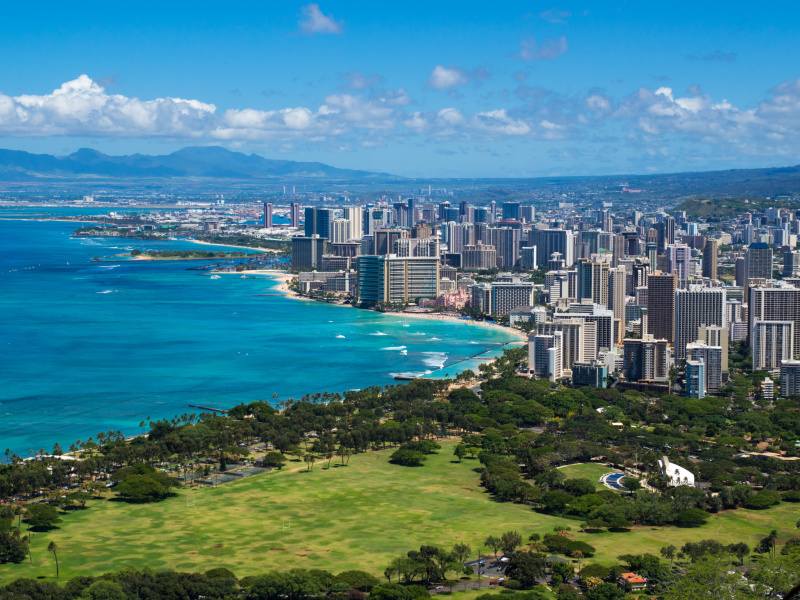

Honolulu, Hawaii
3. Carson City, Nevada: Carson City, the capital of Nevada, is another example of a state capital not directly served by interstates. While the city is in close proximity to Reno, which has interstate connectivity, Carson City does not have a direct interstate connection. Instead, it relies on state routes and local roads for transportation.
III. Implications and Challenges:
The absence of direct interstate access in these state capitals poses several challenges and implications:
1. Transportation Costs: Without interstate connectivity, transportation costs can be higher for both businesses and individuals. The lack of efficient freight routes may lead to increased prices for goods and services, impacting the local economy. Additionally, residents and tourists may face higher travel expenses due to limited transportation options.
2. Economic Development: Interstate highways often serve as catalysts for economic development and attract businesses to regions with easy access to transportation networks. State capitals without direct interstate connectivity may face challenges in attracting and retaining businesses, which can hinder economic growth and job opportunities.
3. Emergency Response and Evacuation: During emergencies such as natural disasters or large-scale events, interstate highways are crucial for evacuation and swift response. State capitals without interstates may encounter difficulties in organizing effective evacuation plans, potentially putting residents at risk.
IV. Alternative Transportation Options:
Although these state capitals lack direct interstate access, alternative transportation options play a vital role in their connectivity:
1. Air Travel: Airports serve as essential gateways for these capitals. Well-connected airports ensure efficient travel to and from the cities, providing an alternative to interstate highways.

Air Travel
2. Waterways and Ports: For capitals like Juneau, waterways serve as vital transportation routes. Ports enable trade and passenger travel, ensuring connectivity with the rest of the country and the world.
3. Rail and Local Roads: Railways and local road networks play a significant role in connecting these capitals to neighboring cities and towns within the state. They provide essential transportation links for both residents and businesses.
V. Conclusion:
While interstates are a crucial component of America's transportation infrastructure, several state capitals do not have direct access to this extensive network. The absence of interstate connectivity presents unique challenges and implications for these capitals, affecting transportation costs, economic development, and emergency response.
However, alternative transportation options such as air travel, waterways, rail, and local roads help bridge the connectivity gap. Understanding the intricacies of transportation infrastructure in these state capitals is essential for policymakers, residents, and businesses to address the challenges and ensure effective connectivity for the future.