Which Particle is J.J. Thomson Credited with Discovering? Electron, Neutron, Proton, or Photon?
The field of particle physics has witnessed numerous groundbreaking discoveries over the years, unraveling the mysteries of the fundamental building blocks of matter. Among the pioneers in this field is Sir Joseph John Thomson, commonly known as J.J. Thomson. His contributions to the understanding of atomic structure and the discovery of particles have had a profound impact on the scientific community. In this article, we will delve into the specific particle that J.J. Thomson is credited with discovering, exploring its properties, and shedding light on its significance in the world of physics.
1. J.J. Thomson's Life and Achievements
Before diving into the particle discovery, let's briefly examine J.J. Thomson's life and notable achievements. Born in 1856 in England, Thomson made significant contributions to the field of physics. He is best known for his experiments related to cathode rays, which eventually led to the identification of the particle in question. Thomson's work earned him the Nobel Prize in Physics in 1906, solidifying his position as a leading figure in the scientific community.
JJ. Thomson lived 1856 – 1940
2. The Discovery of the Electron
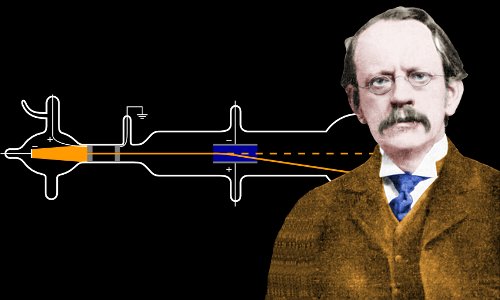
J.J. Thomson's most significant contribution to particle physics is the discovery of the electron. Through his experiments with cathode rays, Thomson demonstrated that they were composed of negatively charged particles. These particles were later named electrons, derived from the Greek word "elektron," meaning amber. Thomson's experiments paved the way for a better understanding of atomic structure, revealing that atoms consist of smaller, indivisible particles.

J. J. Thomson in his laboratory operating a cathode ray tube
3. Characteristics and Significance of Electrons
Electrons are elementary particles with a negative charge and a mass approximately 1/1836th that of a proton. They are found in orbit around atomic nuclei and play a crucial role in determining the chemical properties of elements. Electrons are responsible for chemical bonding and are essential for the functioning of electronic devices. Thomson's discovery of the electron revolutionized the field of physics, forming the basis for the development of quantum mechanics and laying the groundwork for modern technology.

A cathode ray tube, similar to that used by J. J. Thomson
4. The Neutron and Proton: Other Fundamental Particles
While J.J. Thomson is renowned for his discovery of the electron, he is not credited with the discovery of the neutron and proton. These particles were later identified by James Chadwick and Ernest Rutherford, respectively. The neutron, which has no charge, was discovered in 1932 by Chadwick, while the proton, with a positive charge, was identified by Rutherford in 1919. Both the neutron and proton are integral components of atomic nuclei, contributing to the overall mass and stability of atoms.
5. The Photon: A Quantum of Electromagnetic Radiation
Although not directly associated with J.J. Thomson's discoveries, it is worth mentioning the photon in the context of fundamental particles. The photon is the quantum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, X-rays, and radio waves. Albert Einstein's groundbreaking work on the photoelectric effect in 1905 helped establish the existence of photons. Photons have zero rest mass and travel at the speed of light. They play a central role in the field of quantum mechanics, explaining the wave-particle duality of light.
In conclusion, J.J. Thomson is primarily credited with the discovery of the electron, a fundamental particle with a negative charge. His experiments with cathode rays led to the identification of electrons and significantly contributed to our understanding of atomic structure. While Thomson's discoveries focused on electrons, other fundamental particles such as the neutron and proton were discovered by subsequent scientists. Additionally, the photon, though not directly related to Thomson's work, is another important particle in the realm of quantum mechanics. By unraveling the mysteries of these particles, scientists continue to deepen their understanding of the fundamental nature of the universe.