Unveiling the Slippery Texture of Soap: Which Substance Contributes?
Soap, a daily essential in our lives, has a unique slippery texture that leaves our skin feeling clean and refreshed. Have you ever wondered what makes soap so slippery? In this article, we will explore the substances that contribute to soap's slippery texture, unraveling the science behind this common household item.

Which of these substances contributes to soap’s slippery texture?
1. Understanding Soap's Composition:
Introduce the basic composition of soap, highlighting its primary ingredients.
Discuss the combination of fats or oils with an alkali, which undergoes a chemical reaction known as saponification to form soap.
Emphasize the role of fatty acids and their influence on soap's properties.
2. The Role of Surfactants:
Explain the concept of surfactants and their significance in soap production.
Describe how surfactants reduce the surface tension of water, allowing it to interact more effectively with dirt and oils on the skin. Discuss how the presence of surfactants affects soap's slippery texture.
3. The Slippery Nature of Glycerin:
Explore the role of glycerin in soap's slipperiness. Highlight the fact that glycerin is a natural byproduct of the saponification process. Discuss how glycerin acts as a humectant, attracting and retaining moisture on the skin, contributing to the slippery feel of soap.
4. Sodium Stearate and Soap's Slipperiness:
Examine the specific substance, sodium stearate, and its contribution to soap's slippery texture. Explain that sodium stearate is a common fatty acid salt derived from the saponification process. Discuss how the arrangement of sodium stearate molecules on the skin's surface reduces friction, resulting in a slippery sensation.
5. Other Slip-Enhancing Additives:
Discuss additional substances that may be added to soap formulations to enhance its slipperiness. Mention ingredients such as oils, emollients, or synthetic additives that can contribute to a smoother texture and improved glide during use.
6. The Importance of Water:
Highlight the role of water in soap's slipperiness. Explain how the presence of water molecules between the soap and the skin further reduces friction, enhancing the slippery feel. Discuss the importance of wetting the soap before use to activate its lubricating properties.
7. Soap Formulations and Slipperiness:
Address the fact that different soap formulations may vary in their slipperiness. Mention that the specific combination and concentration of ingredients, as well as the manufacturing process, can influence the overall texture and feel of the soap.
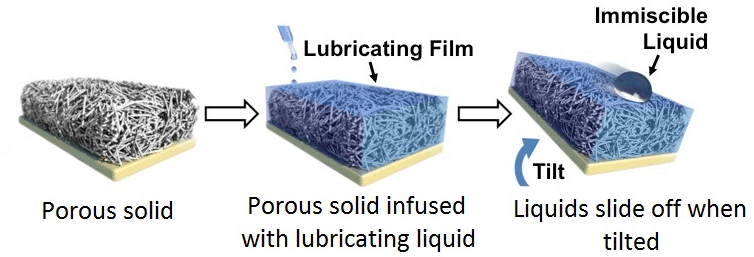
Example of which of slippery liquid infused surface
Summarize the key points discussed in the article, emphasizing the substances that contribute to soap's slippery texture. Highlight the role of surfactants, glycerin, sodium stearate, and water in creating the desired sensation. Encourage readers to appreciate the science behind soap's slipperiness and the importance of these substances in enhancing our daily cleansing experience.