Understanding the Synergy Between Gravity and Inertia: Explained
Gravity and inertia are fundamental concepts in physics that play a crucial role in understanding the motion of objects in our universe. In this article, we will explore how gravity and inertia work together to govern the behavior of objects and the motion of celestial bodies. By delving into the relationship between these two forces, we can gain a deeper understanding of the mechanics behind the movement of planets, moons, and even everyday objects on Earth.
Mass, weight and Gravity
1. The Basics of Gravity:
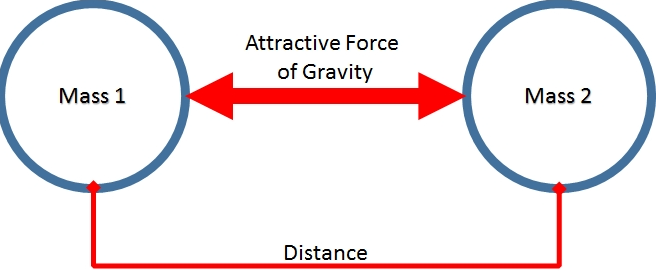
Provide a brief explanation of gravity as a force that attracts objects with mass towards each other.
Discuss how gravity is responsible for keeping celestial bodies, such as planets, in their orbits around the Sun, and how it influences the motion of objects on Earth.
2. Introducing Inertia:
Introduce inertia as the property of an object to resist changes in its motion. Explain that an object at rest tends to stay at rest, while an object in motion tends to stay in motion with the same speed and direction unless acted upon by an external force.
3. Newton's First Law of Motion:
Discuss Newton's first law of motion, also known as the law of inertia, which states that an object will remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. Emphasize how inertia provides the initial resistance to any changes in motion.
4. Gravity and Inertia in Celestial Motion:
Explain how gravity and inertia work together in celestial motion. Describe how gravity pulls objects towards each other, while inertia resists changes in their motion. Provide examples such as the Earth's orbit around the Sun, where gravity provides the centripetal force that keeps the Earth in its path, while inertia keeps the Earth moving at a constant speed.
5. Falling Objects on Earth:
Illustrate how gravity and inertia collaborate in the motion of falling objects on Earth. Discuss how gravity pulls objects downward, overcoming their initial inertia and causing them to accelerate towards the ground. Explain how the force of gravity and the resistance of inertia determine the speed and trajectory of a falling object.
6. Projectile Motion:
Discuss how gravity and inertia interact in projectile motion. Explain that when an object is thrown or launched into the air, it follows a curved trajectory due to the combined effects of gravity pulling it downward and inertia maintaining its horizontal motion. Use examples like a thrown ball or a launched rocket to demonstrate this concept.
7. Orbits and Escape Velocity:
Explain how gravity and inertia work in harmony to establish stable orbits around celestial bodies. Discuss the concept of escape velocity, the minimum velocity required for an object to overcome gravity's pull and escape the gravitational field of a planet or celestial body. Highlight how gravity keeps objects in orbit by continuously pulling them inward, while inertia allows them to maintain their forward motion.
8. Application in Space Exploration:
Discuss the practical applications of understanding the interplay between gravity and inertia in space exploration. Explain how spacecraft use gravitational assists from celestial bodies to gain speed and change trajectories, utilizing the principles of gravity and inertia to optimize their missions.
9. Everyday Examples:
Provide relatable examples from daily life to further illustrate the collaboration between gravity and inertia. For instance, explain how inertia causes passengers to lurch forward when a moving vehicle suddenly stops and how gravity pulls objects downwards when dropped from a height.
How do gravity and inertia affect our lives?
Summarize the article by reiterating the importance of gravity and inertia and their interdependence. Emphasize that gravity acts as the force of attraction, while inertia resists changes in motion. Together, these forces shape the behavior of objects and govern the motion of celestial bodies, providing a foundation for understanding the mechanics of our universe.